- Acupuncture
- Durable Medical Equipment
- Foot and Ankle
- General Orthopedics
- Hand and Wrist
- Hip Preservation
- Joint Replacement
- Massage Therapy
- MRI
- Neck and Back
- Occupational Therapy
- Orthobiologics
- Physical Therapy
- Robotically Assisted Technology
- Shoulder and Elbow
- Sports Medicine
- Sports Nutrition
- Synergy Surgery Center ASC
A TEAM THAT MOVES YOU FORWARD
Orthobiologics is a field of medicine that uses natural substances derived from the body to help heal and regenerate tissues, reduce inflammation, and alleviate pain. These treatments harness the body’s own healing abilities and are commonly used by Synergy Orthopedics’ sports medicine specialists to treat injuries and degenerative conditions when appropriate.
For more information call:
858-412-6080
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP)
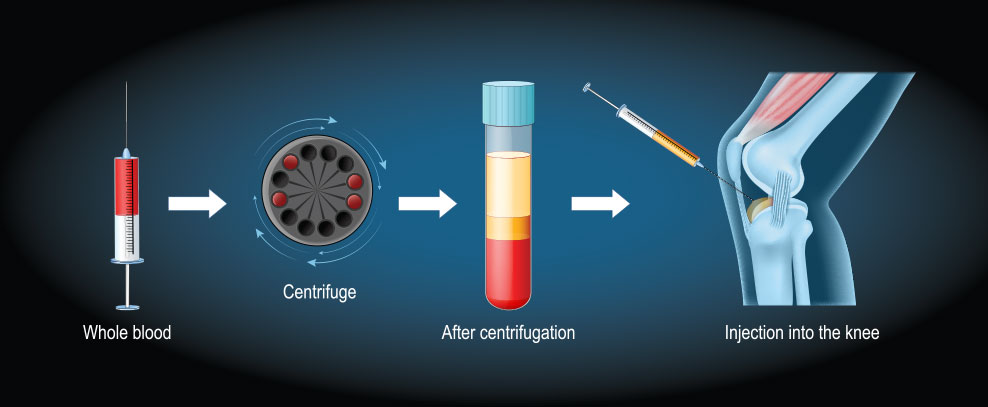
PRP is a regenerative medicine that harnesses and amplifies growth factors created by blood cells. It contains increased levels of platelets and growth factors, which can reduce inflammation and help with healing. It is best to stop taking aspirin, anti-inflammatory medications, or other blood-thinning medications for 5 days after a PRP injection. Tell your doctor if you take any aspirin or blood-thinning medication before your PRP treatment.
A healthcare team member will draw a test tube of your blood. The blood sample will be placed into a centrifuge, which separates the platelets from the other blood cells. The separated platelets are then injected into the injured area.
Cost: $650 for one extremity or $800 for two extremities
Adipose (Fat) Stem Cell
Adipose tissue is a fat tissue that contains your own stem cells. Harvested adipose tissue is resized and washed into microfat containing a concentration of these cells, which can promote the natural healing of damaged or injured tissue.
It is best to stop taking aspirin, anti-inflammatory medications, or other blood-thinning medications for 5 days after a stem cell injection. Tell your doctor if you take any aspirin or blood-thinning medication before treatment.
Your doctor will harvest the tissue through a small incision. The adipose tissue is collected into a syringe. After washing and filtrating the microfat, the collected cells will be injected.
Cost: $3,500
Bone Marrow Concentrate (BMAC)
Your own bone marrow contains stem cells, PRP, and other growth factors. Bone Marrow Aspirate Concentrate is a procedure that harvests your own bone marrow and isolates these cells and cell products that help heal injured tissue.
It is best to stop aspirin, anti-inflammatory medication, or other blood-thinning medication for 5 days after a BMAC injection. Tell your doctor if you take any aspirin or blood-thinning medication before treatment.
Your doctor will utilize a needle to draw up bone marrow (usually from the pelvis bone). A centrifuge is used to concentrate the desired cells in your bone marrow. The collected cells and proteins are then injected at the site of injury.
Cost: $2,500
Allogenic Tissue Injection
Human tissue from healthy donors can be used to augment or support regeneration in your own body. One of the more common sources of Orthobiologics tissue is the human placenta or umbilical cord. Such treatment often has structural and functional components, such as collagen, proteins, and growth factors, which can provide the building blocks our bodies need to recover from injury or surgery.
Cost: $1200 small or $1600 large
Hyaluronic Acid Injection (HA)
Hyaluronic acid is a natural lubricant and filler that helps reduce pain in arthritic joints by reducing friction and reducing inflammation in arthritic joints. This treatment often involves two options: a series of 3 injections performed about a week apart and a single injection which has high concentration of Hyaluronic Acid.
Cost: 3 injection series at $200 each or a one-time injection for $675.